-RNA is structurally similar to DNA!
-Both nucleic acids are sugar-phosphate polymers and both have nitrogen bases attached to the sugars of the backbone- but RNA is usually single-stranded.
there are differnces between DNA & RNA, they are :
1- The sugar in RNA is ribose,While DNA contains deoxyribose.
2- Unlike double-stranded DNA, RNA is usually single-stranded. However, RNA can form intrastrand double helixes, as in tRNA.
3- DNA nucleotides include Adenine, Guanine, Thymine or Cytosine whereas RNA nucleotides uracil is present instead of thymine.
4- RNA molecules are shorter than DNA molecules.
Types of RNA
- Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs)
they are called ribosomes, exist outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm of a cell. The ribosome structure is composed of 2 subunits. A small and a large subunit.
Each ribosome is a complex consisting of about 60% ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 40% protein.
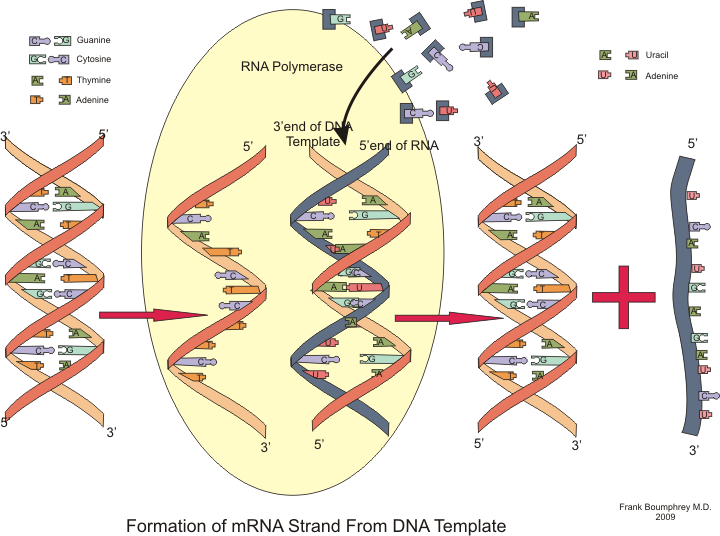
- Messenger RNAs (mRNAs)
firstly, DNA is transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into a protein product.
these mRNAs record information from DNA in the cell nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes which found in cytoplasm.
- Transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
Transfer RNAs are encoded by genes that also encode for the 5S size rRNA.
Transfer RNAs are encoded by genes that also encode for the 5S size rRNA.
their function is to deliver amino acids one by one to protein chains growing at ribosomes.
- Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
they are Known as short interfering RNAs, a class of double stranded RNA molecules involved in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. they interfere with the expression of specific genes controlling the stability of the mRNA. In this way the mRNA is disintegrated (when necessary) to avoid its overexpression with a consequent overproduction of proteins.
- Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs)
They are transcribed by two ways, either RNA polymerase II along
with mRNA or by RNA polymerase III along with all nuclear tRNAs and the
5S rRNA.
They are primarily involved in mRNA processing such as splicing by
removal of introns from pre−mRNA and also in maintenance of the
telomeres.
- Heterogeneous nuclear RNAs (hnRNAs)
hnRNA is an immature single strand of mRNA.




0 التعليقات:
Post a Comment