DNA sequencing is the process of determining the accurate order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
DNA Sequencing requires various techniques and methods that are used to define the sequence of the nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule.
The most common method for performance this is called the dideoxy method or Sanger method.
this method is named Sanger method after its inventor, Frederick Sanger, who was awarded Nobel prize in chemistry for this achievement in1980.
The Need for DNA Sequencing
1- DNA sequencing may be used to determine the sequence of individual genes, larger genetic regions (i.e. clusters of genes or operons), whole genomes.
2- Sequencing may provide, Depending on the methods used, the order of nucleotides in DNA or RNA isolated from living organisms cells such as animals, plants, bacteria, archaea, or virtually any other source of genetic information.
2- Sequencing may provide, Depending on the methods used, the order of nucleotides in DNA or RNA isolated from living organisms cells such as animals, plants, bacteria, archaea, or virtually any other source of genetic information.
3- Researchers may use the product sequences in molecular biology or genetics to further scientific progress or may be used by medical staff to make treatment decisions or aid in genetic counseling.
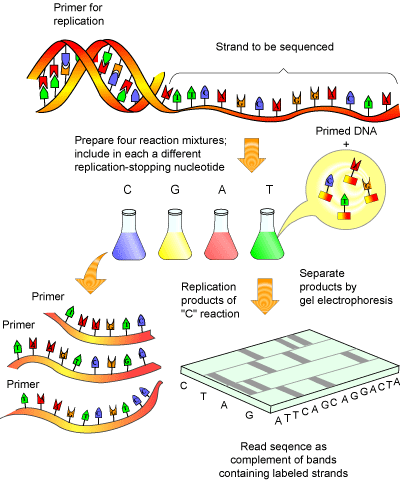
The Procedure
- At the beginning, The DNA should be prepared as a single strand to be sequenced.
- The DNA template is supplied with :






0 التعليقات:
Post a Comment